

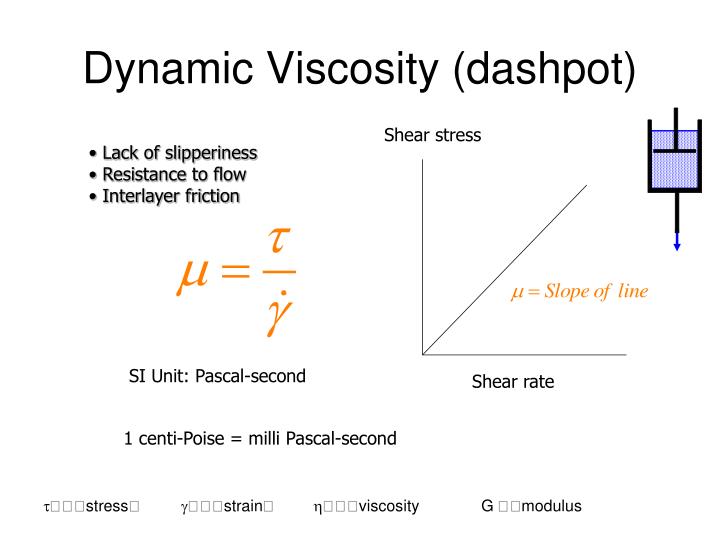
Thus, as one plate is moved at a given velocity V (called the shear rate) relative to the other plate, a distribution of fluid velocities is created. It is the nature of a viscous fluid to attach itself to the surfaces of these plates. As with most derived measurements in the science of engineering, a model is required.Ĭonsider two plates moving parallel to each other separated a given distance (y) by a viscous fluid. Viscosity is actually a measurement of internal friction, or resistance, to flow by external forces. All other fluids are then measured, calibrated, and thus compared to the viscosity of water. Water at approximately 70☏ (21☌) has an absolute viscosity of about one centipoise. Molasses and motor oil are thick or high viscosity liquids while gasoline and water are thin, low viscosity liquids. Thick liquids are said to have a high viscosity and thin liquids a low viscosity. Viscosity can also be thought of as a measure of the "thickness" of the liquid. Thinner liquids, such as water, have lower viscosities, while thicker liquids like oil have higher viscosities. Viscosity is the measure of a fluid's resistance to flow.

Viscosity measurements are used in everything from lubrication and heat transfer fluids, to adhesives and coatings to aerodynamic and hydrodynamic drag. One of the more obscure and confusing parameters is viscosity. These behaviors are defined by a collection of measurements. There is a branch of science called Rheology that deals with the deformation and flow of materials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
